Post Time:Dec 31,2020Classify:Industry NewsView:2192
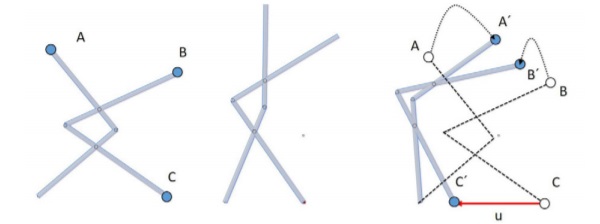
Multiplicators are used to increase the efficiency of a system. Mechanical motion driven by the actuator is a product of force and path. As an example, a small displacement u of point C to C′ is transformed to scaled movement of points A to A′ and B to B′, as in the lever system shown in figure 4. Depending on the geometry the transformation may be set as desired. Generally multiplying units can be built as gears, belt drives and others and can also be used as a force multiplying process which can be carried out in a rotary or linear fashion. [3] The most impressive way to work with adaptive systems is by using autonomous elements. Self-regulation of those systems is the result of the correct combination of various components and the purpose is to create autonomous façade applications. Two strategies of adapting façades are described in the following sub-categories: the transparency of façades as well as the way façade applications can be moved, both of which can be carried out autonomously Primarily, the function of façades is to separate the interior and exterior. Furthermore, aesthetics and design are of architectural importance and structural-physical values are responsible for comfort. Even if the level of transparency in façades is relevant for the light intensity in the room, they cannot protect from overheating due to solarisation. Therefore, creating autonomous regulation is a factor to save energy over the entire life cycle. Thermochromic resin layers with nanocapsule structure, located between the glass layers, can be used as a switching tool. The level of transparency is a result of the nanostructure, which enables solar radiation to pass through the resin layer. In order to achieve the switching temperature, the structure of the nanocapsules change and become diffused which, in turn, increases reflection. [4] & [5] Multiplicators
Adaptive Systems
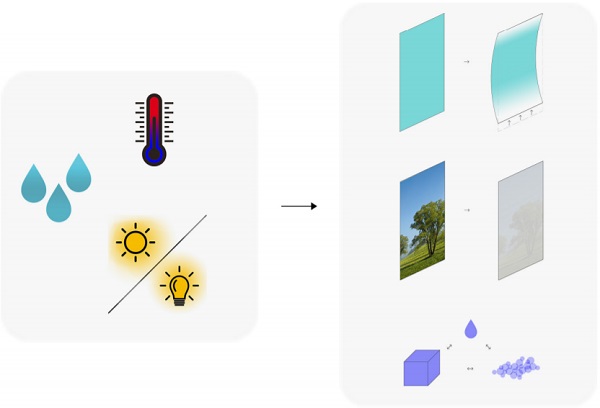
View
![Figure 6 Functional principle of thermotropic laminated glass, [4]](https://www.glassonweb.com/sites/default/files/inline-images/Fig6_22.jpg)
![Figure 7 Thermochromic glazing in low (a) and high (b) temperature state, [6]](https://www.glassonweb.com/sites/default/files/inline-images/Fig7_20.jpg)
Source: Author: shangyi
PrevThe market scale of Chinas glass industry exceeds 100 billion
Asahi India Glass rating: Buy; new import duties to help the companyNext